How to bindService from shell
在Android ROM测试过程中遇到的一个有意思的漏洞链利用场景:
-
一个不导出的/受权限保护的service组件存在漏洞,漏洞的利用需要bindService后触发。(
onBind返回一个IBinder) -
现在有一个
Runtime.exec产生的system命令执行,要如何触发Context.bindService?
先抛一个问题:
adb shell下的
am命令中有start-acvity,start-service,为什么没有bind-service?
ActivityManager的接口如下 ,其中 IApplicationThread 是app主线程AcvityThread创建的一个binder,使得AMS可以管理applicaon。
//IActivityManager.aidl
int bindIsolatedService(in IApplicationThread caller, in IBinder token, in Intent service,in String resolvedType, in IServiceConnection connection, int flags, in String instanceName, in String callingPackage, int userId);
AMS服务端代码片段如下,根据传入的 IApplicationThread 查找是否有对应的 ProcessRecord ,没找到的话会抛出异常。
start-activity 和 start-service 允许传入的 IApplicationThread 为空。这样就不难理解为什么am命令中有 start-activity , start-server , start-service 但是没有 bind-service 了。直接从shell fork出来的进程没有有效的 IApplicationThread ,无法通过校验。
//com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service, String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String instanceName, String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp == null) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + callingPid
+ ") when binding service " + service);
}
//...
final boolean isCallerSystem = callerApp.info.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID;
//...
ServiceLookupResult res = retrieveServiceLocked(service, instanceName, resolvedType, callingPackage, callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, isBindExternal, allowInstant);
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
//...
mAm.startAssociationLocked(callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName, callerApp.getCurProcState(), s.appInfo.uid, s.appInfo.longVersionCode, s.instanceName, s.processName);
//...
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity, connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent, callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName, callingPackage);
//...
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);
继续仔细分析发现, retrieveServiceLocked 在根据Intent查找对应的Service时,使用来自Binder的callingUid进行
权限判定,而不是根据 IApplicationThread 查到的 callerApp.info.uid 。并且这里没有验证来自Binder的callingUid是否和 callerApp.info.uid 相等。直到 IServiceConnection 的connected被调用,AMS都是使用
callerApp,没有再使用callingUid。
//com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private ServiceLookupResult retrieveServiceLocked(Intent service, String instanceName, String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int callingPid, int callingUid, int userId, boolean createIfNeeded, boolean callingFromFg, boolean isBindExternal, boolean allowInstant) {
ServiceRecord r = null;
//...
if (mAm.checkComponentPermission(r.permission,
callingPid, callingUid, r.appInfo.uid, r.exported) != PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
if (!r.exported) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Permission Denial: Accessing service " + r.shortInstanceName
+ " from pid=" + callingPid
+ ", uid=" + callingUid
+ " that is not exported from uid " + r.appInfo.uid);
return new ServiceLookupResult(null, "not exported from uid "
+ r.appInfo.uid);
//android/app/ActivityManager.java
public static int checkComponentPermission(String permission, int uid, int owningUid, boolean exported) {
// Root, system server get to do everything.
final int appId = UserHandle.getAppId(uid);
if (appId == Process.ROOT_UID || appId == Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
return PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED;
}
总结:
AMS允许访问bindService接口的binder callingUid和传入的参数IApplicationThread不是来自同一个uid, callingUid决定了能否访问目标服务
更准确的问题是:
How to bindService from (system) shell (with normal app)?
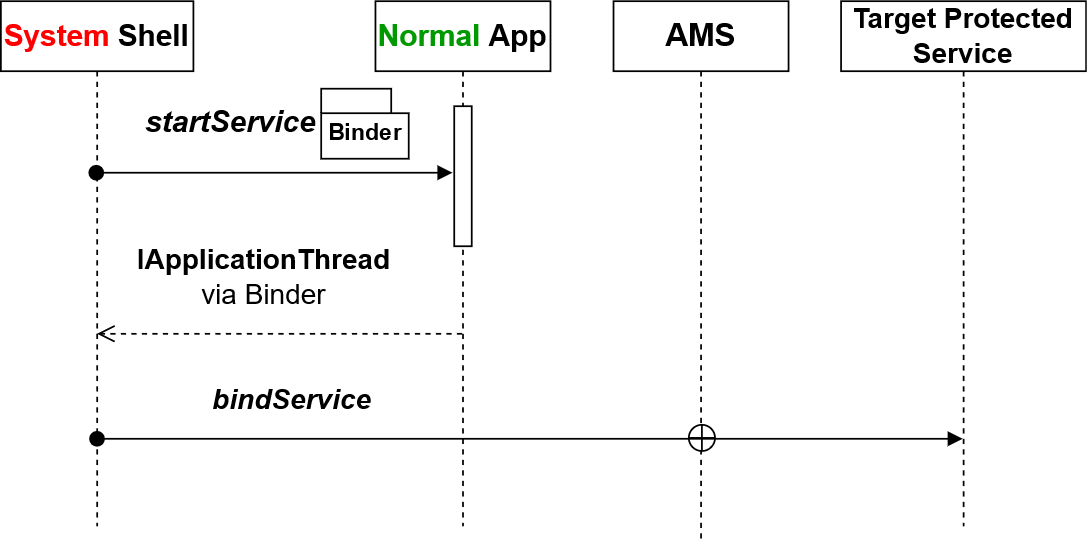
我们可以用system shell向AMS发起 bindService 请求, IApplicationThread 参数借用我们可控的低权限App的 IApplicationThread 。AMS权限认证结果是system权限,因此我们可以访问受厂商权限保护的service。
过程如下:
- 一个system shell,同时我们还有一个低权限普通app。
- 类似于am命令的方式,system shell用
/system/bin/app_process执行jar包,将一个Binder通过startService的方式发送给普通app - 普通app把自己的
IApplicationThread回传给system shell - System shell借到
IApplicationThread后,向AMS发送 bindService 请求, 在IServiceConnection的回调connected中获得目标服务的IBinder
其中第二、三步是为了把普通App的IApplicationThread传给system shell,我没想到特别好的方式,还是用binder传了一下。借用IApplicationThread其实就是借用一个Context用来实现bindService,(参考ContextImpl中bindServiceCommon),IApplicationThread只是被Context封装了。